Display campaigns can be difficult when it comes to targeting the right audience. In fact, many campaigns end up utilizing a single main targeting type such as:
- Keywords
- Topics
- Interests/behavior through affinity or in-market segments
- Managed placements
These are all great strategies, but can still leave the targeting broader than we would prefer. In tandem, we can use negative placements as a key tactic to exclude irrelevant traffic. However, there is another approach that can be used to help limit the amount of time that is needed to sift through placement reports and allow more time to focus our efforts on optimizing and analyzing targeting methods.
In this post, you will learn 5 ways to improve your Display strategy with multi-layered targeting. We will review the targeting approach, examples, and recommendations to properly target and bid each layer.
1) Keywords And Topics
Keywords are the most specific targeting type as they are used to trigger pages on websites that speak specifically to that keyword’s theme. Therefore, showing your ads to your target audience. This strategy works in theory, but have you ever taken a look at the placements report and wonder why a particular site was even listed as serving an ad? This is because it’s not looking for topically relevant sites or pages, but only specific parts of the content that are relevant based on the keyword alone.
This is where layering in topics comes into play. By specifying the topic, the website also has to be in the genre that you specify to help narrow in on your audience and where they will be on the web. This layering also helps cue ads to not only a paragraph or page but on the most relevant page of a topically relevant site.
Example
Utilize topics related to your brand to limit exposure on random articles and even spam. These pages and sites must be classified within that target topic along while showing the keywords listed.
Targeting And Bid Recommendation
I recommend utilizing keywords as the first layer for target and bid. Ultimately, we want pages that are relevant to our keywords vs the broader spectrum of the topics themselves, as these do not get as granular. With that, use “bid only” on the topic targeting to allow for separate bids or bid adjustments based on the traffic and quality of data.
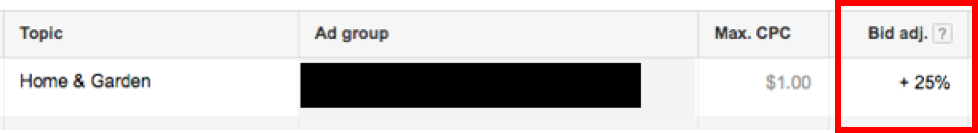
2) Keywords And Interests
The “keywords and interests” layered approach is similar to keywords and topics, except that instead of relying on the topics to hone in on the sites we show, we allow the keywords to provide that information while using interests to focus more on finding the right audience.
By utilizing interests as well as keywords, we can find an in-market list for target users or find the ideal audience at scale with affinity audiences. You can also create custom affinity audiences to combine interests by keyword and domain targets to find the right audience. If you want to learn more about creating a custom affinity audience you can read “3 Killer Strategies For Custom Affinity Audience Campaigns.”
Example
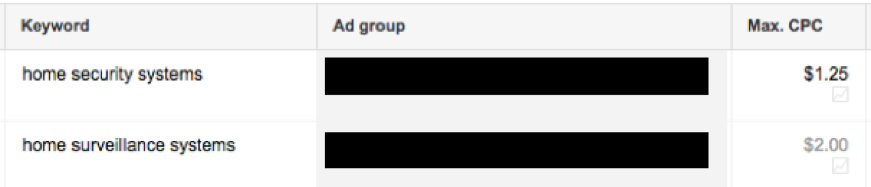
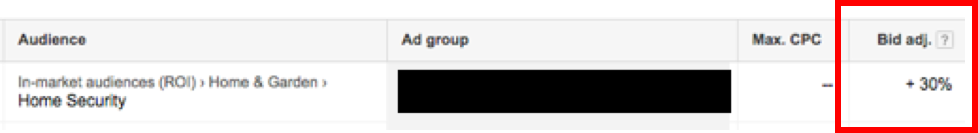
For this example, we will use home security. The goal of this campaign is to target people looking at pages around security systems and have an interest in home security. We can use keywords to find relevant pages regarding home security and home surveillance systems, while utilizing the in-market audience for ‘Home Security’ with a bid adjustment based on the keyword bid.
![]()
Recommendation
Utilize keywords to find pages relevant to our target user while utilizing “bid only” for interest/behavior as these are a segment of users more ready to buy the product or service. The in-market audience segment will then help place those ads and put higher priority when our specified users are on those pages surrounding the keywords.
3) Managed Placements And Interests
Managed placements is a great strategy to utilize when there are specific websites you know that users who relate to the brand will be visiting. To make this even more advantageous, adding an in-market segment can help narrow the audience to be more effective.
Example
For our home security company, we want to place ads on tech websites and focus on pages relevant to a buyer’s guide, gear reviews, and other relevant pages. To then make sure those ads are shown to those more likely to click on the ad, we will then layer an in-market audience for ‘Home Security’, showing ads to visitors who are researching and ready to buy our product or service. This now gives us a layered strategy that is showing ads on a relevant page of a technology website and showing those ads to an interested user.
4) Demographics Layers
Demographics are a needed second or third targeting layer based on the desired profile of the user. If a product or service can be used or purchased by anyone, still adding in all demographics can then allow for exclusions or bid adjustments based on the data analysis of each age range, gender, or parental status. If our product or service does have a target demographic, we can either tailor the audience to only show to users within that demographic or place initial bid adjustments to optimize towards the target audience.
Example
If there is a known demographic range; starting out by limiting the demographic information to this range can help reduce unwanted traffic. Then, optimize the remaining segments based on performance.
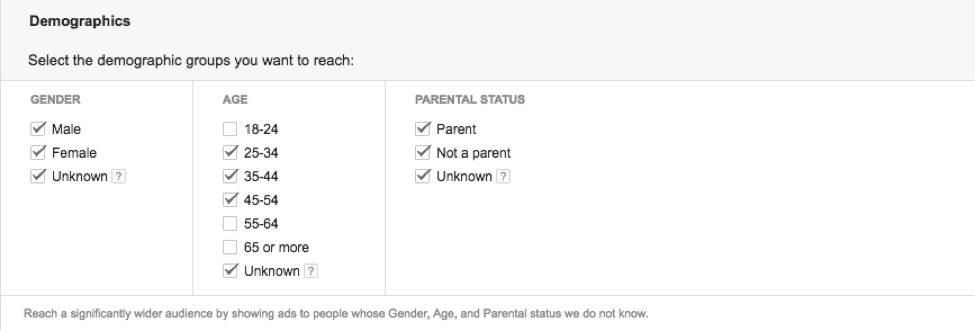
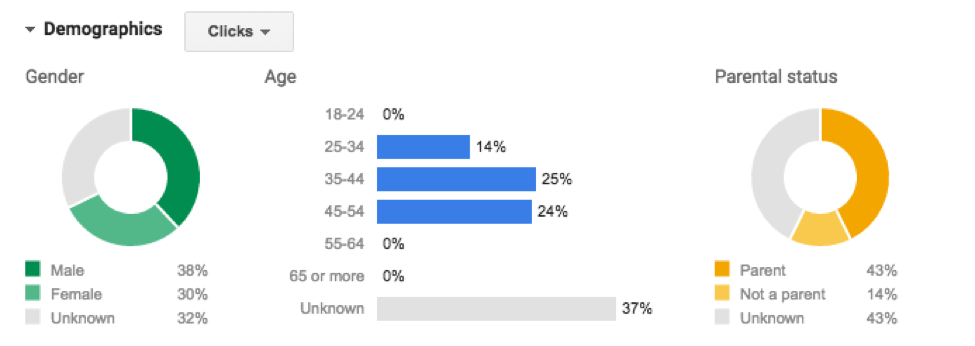
Based on the data, we can see that we want to add a higher bid adjustment to our 35-44 and 45-54 age ranges while focusing more on Parents. In this scenario, gender is still too close to make any major optimizations, but we may want to bid slightly higher for a male vs female user.
Recommendation
Demographics cannot be the first layer with target and bid, but can utilize a custom bid within that demographic target or a bid adjustment based on the data for each target. I recommend using bid adjustments to help keep easier tabs on the amount of actual bids being used.

5) Exclusions And Site Category Options
Lastly, exclusions for both targeting and site categories are another must-have approach to any layered Display targeting. Each targeting type includes a campaign exclusion option. These options include topics, keywords, interests & remarketing, and demographics.
Targeting Exclusion Example
If we are to only target Display keywords because of being uncertain of what to add for the second layer we could either add negative topics we know our prospective customers would not visit, or exclude interests that our users would not have, based on market research. We could also exclude the specific sites from the placement reports that we touched on earlier.
Remarketing Exclusion Example
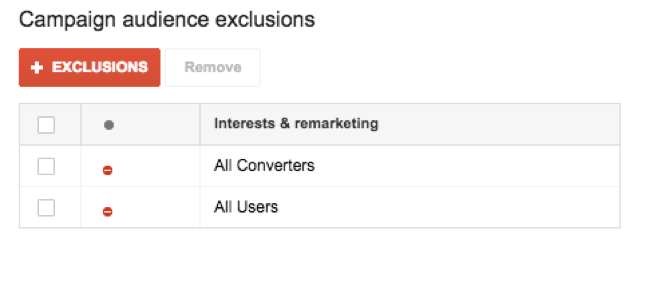
I saved excluding remarketing lists for last because, outside of site categories, this is a must in order to not overlap any remarketing, brand awareness, or first-touch acquisition Display campaigns. If you have a typical remarketing list, you are already targeting all site visitors and excluding all converters. So, we want to do a similar exclusion with our non-remarketing Display campaigns to allow the remarketing campaigns to target current visitors. This takes away any potentially competing ad sets due to a user being in our target audience plus our remarketing lists.
Making this a priority will allow remarketing and current customer (converters) remarketing campaigns to display more specific ad messaging based on the user’s website visit behavior.
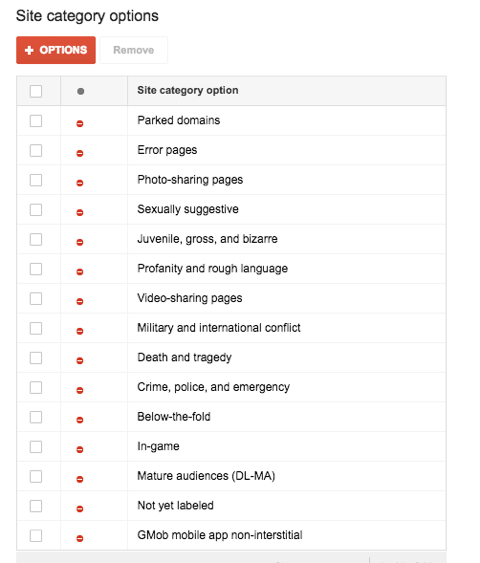
Site Category Options
Site category options give plenty of ways to exclude topics, site categories and specified content you would not want to associate with your brand. These categories can be related to crime, death, profanity, video ads and mobile app ads. Based on your brand, these categories will change, but in general, removing categories are a good exclusion layer to protect your Display investment.
Recommendation
If any exclusions are added, remarketing lists and site exclusions are the top recommendations. Removing visitors, customers, and unwanted site categories are essential to finding only new, relevant prospects.
Conclusion
Display campaigns can prove harder to show good performance, but by utilizing multiple targeting layers, it will help improve upon the types of optimizations being performed and better match the ideal customer. By applying these 5 targeting layer methods, you will ultimately center on a strategy that creates more successful Display campaigns.